Light therapy has emerged as a powerful tool in the fields of health, wellness, and skincare, offering a range of benefits by harnessing the natural energy of light. With its non-invasive nature and growing body of research, light therapy has gained popularity among both professionals and individuals seeking effective solutions for various conditions. Among the different types of light therapy, red, infrared, and blue light stand out for their unique properties and targeted benefits. Each type of light operates at specific wavelengths, penetrating the skin and tissues to varying degrees and addressing distinct needs.
This article aims to compare and contrast these three types of light therapy, exploring their specific benefits, common uses, and how they work at the cellular level. Whether you’re looking to rejuvenate your skin, alleviate pain, or treat acne, understanding the differences between red, infrared, and blue light therapy will help you make an informed decision about which therapy is best suited for your needs.

Red Light Therapy
Red light therapy, also known as photobiomodulation, operates within the wavelength range of 620nm to 700nm. This type of light penetrates the skin to a medium depth, reaching the dermis where it stimulates cellular activity. Red light is particularly effective for enhancing skin health, promoting collagen production, and reducing inflammation. It works by energizing the mitochondria, the powerhouse of cells, which boosts cellular repair and regeneration.
Common applications of red light therapy include treating wrinkles, scars, and fine lines, as well as accelerating wound healing. It’s also used to reduce pain and inflammation in muscles and joints. Due to its ability to improve blood circulation and tissue repair, red light therapy is often used in both cosmetic and therapeutic settings.
Understanding how red light interacts with your body can help you decide if it’s the right choice for your needs. Whether you’re looking to improve your skin’s appearance or address deeper tissue concerns, red light therapy offers a versatile and effective solution.
Infrared Red Light Therapy
Infrared red light therapy utilizes light in the near-infrared spectrum, typically within the wavelength range of 700nm to 1000nm. Unlike visible red light, infrared light is invisible to the human eye but penetrates even deeper into the body, reaching muscles, joints, and bones. This deep penetration makes infrared light particularly effective for treating chronic pain, inflammation, and deep tissue injuries.
Infrared light therapy works by increasing blood circulation, enhancing oxygenation of tissues, and promoting the repair of damaged cells. It stimulates the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the energy currency of cells, helping to accelerate healing processes. This makes it a popular choice for athletes looking to recover from injuries, as well as for individuals dealing with chronic conditions like arthritis, tendonitis, or deep muscle pain.
Another significant benefit of infrared red light therapy is its ability to provide warmth and comfort, which can help soothe stiff or sore muscles. It’s also used to enhance skin health by promoting collagen production and reducing the appearance of scars and wrinkles, similar to visible red light therapy but with the added benefit of deeper tissue rejuvenation.
Overall, infrared red light therapy is a powerful tool for both therapeutic and cosmetic applications, offering a non-invasive way to promote healing and relieve pain in the deeper layers of the body.
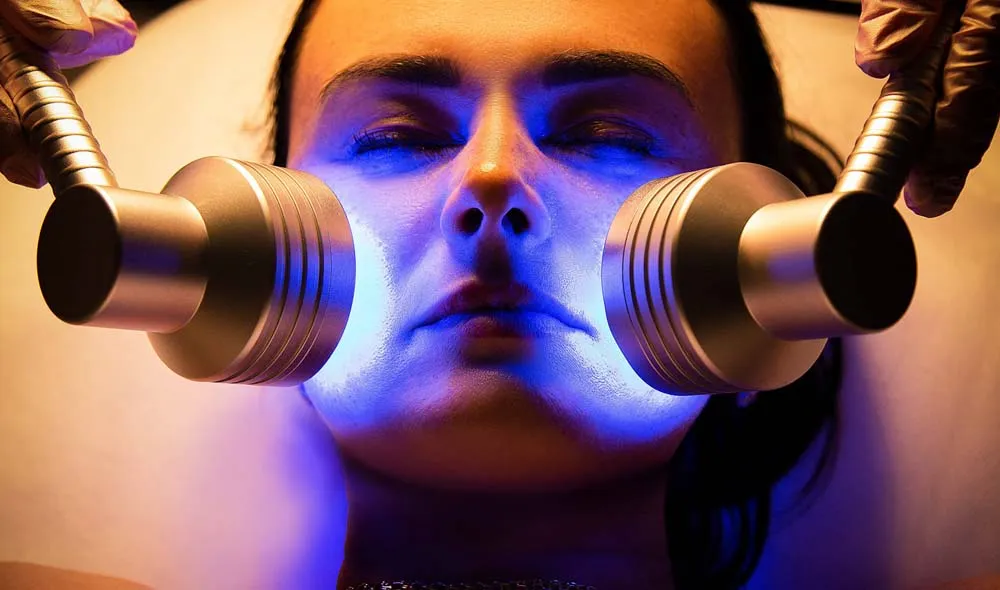
Comparing the Three Types of Light Therapy
When it comes to light therapy, red, infrared red, and blue light each offer distinct benefits and applications, making them suitable for different treatment goals. Here’s a closer look at how they compare:
Wavelength and Skin Penetration
- Red Light Therapy (620nm-750nm): Red light has a medium wavelength that penetrates the skin more deeply than blue light but less than infrared light. It primarily affects the surface and slightly deeper layers, making it ideal for treating skin conditions like wrinkles, fine lines, and promoting collagen production.
- Infrared Red Light Therapy (700nm-1200nm): Infrared red light has the longest wavelength, allowing it to penetrate the deepest into the skin, reaching muscles, joints, and even bones. This deep penetration makes it highly effective for relieving pain, reducing inflammation, and promoting tissue repair at a deeper level.
- Blue Light Therapy (400nm-490nm): Blue light has the shortest wavelength and penetrates only the outermost layer of the skin (the epidermis). It is most effective for targeting surface-level skin issues, particularly acne, by killing acne-causing bacteria and reducing inflammation.
Applications and Benefits
- Red Light Therapy: Known for its anti-aging properties, red light therapy is effective in reducing the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and scars. It also aids in improving skin tone, texture, and overall complexion by boosting collagen and elastin production.
- Infrared Red Light Therapy: This type is widely used for pain management, muscle recovery, and wound healing. Its ability to penetrate deep into the tissue makes it ideal for treating conditions like arthritis, muscle soreness, and even promoting faster recovery from injuries.
- Blue Light Therapy: Primarily used for treating acne, blue light therapy works by eliminating Propionibacterium acnes bacteria on the skin. It’s also being explored for its potential in treating other skin conditions like psoriasis and eczema.
Safety and Side Effects
- Red Light Therapy: Generally considered safe for all skin types, with minimal side effects. It is non-invasive and painless, making it suitable for regular use.
- Infrared Red Light Therapy: Also safe for most people, but because it penetrates deeper, it’s important to follow usage guidelines to avoid overexposure, which can lead to discomfort or overheating of the skin.
- Blue Light Therapy: Safe when used appropriately, but overuse can lead to skin dryness or irritation. Additionally, prolonged exposure to blue light from screens has been linked to sleep disruption and potential eye strain.
Treatment Settings
- Red Light Therapy: Available in a variety of settings, including beauty salons, dermatology clinics, and at-home devices.
- Infrared Red Light Therapy: Often used in clinical settings for physical therapy, sports medicine, and pain management, but also available in home-use devices.
- Blue Light Therapy: Commonly found in dermatology offices for acne treatment, but also available in at-home devices specifically designed for acne-prone skin.
FAQ
For treating spider veins, the most effective LED light color is typically red or infrared light. Here’s why these colors are used:
1. Red Light (660nm)
- Penetration: Red light penetrates the skin at a moderate depth, reaching the superficial blood vessels where spider veins are located.
- Benefits: It can help improve blood circulation, reduce inflammation, and promote healing of the skin. This can contribute to the reduction in the appearance of spider veins over time.
2. Infrared Light (850nm)
- Deeper Penetration: Infrared light penetrates deeper into the skin compared to red light. This deeper penetration can help improve circulation in the underlying tissues and support the repair of blood vessels.
- Benefits: It aids in reducing inflammation and promoting overall tissue health, which can be beneficial for managing spider veins.
Treatment Considerations
- Consistency: Regular use of red or infrared light therapy may be needed to see noticeable improvements in spider veins.
- Consultation: Always consult with a dermatologist or healthcare provider before starting any light therapy treatment for spider veins. They can provide guidance on the most suitable treatment plan and ensure it’s safe for your specific condition.
Yes, using red and blue light therapy together can be beneficial, as each type of light targets different skin issues and can complement each other effectively. Here’s how combining them can be advantageous:
1. Targeting Multiple Skin Concerns
- Red Light Therapy: Primarily addresses deeper skin layers, promoting collagen production, reducing wrinkles, improving skin texture, and aiding in wound healing.
- Blue Light Therapy: Targets surface-level issues such as acne by killing acne-causing bacteria and reducing inflammation.
2. Enhanced Results
Combining red and blue light therapy can provide a comprehensive approach to skin care:
- Red Light Therapy can help with anti-aging and overall skin health, making the skin more resilient.
- Blue Light Therapy can clear up acne and reduce inflammation, leading to a clearer complexion.
3. Treatment Synergy
Using both therapies together can enhance their individual benefits. For instance:
- Blue Light Therapy may reduce acne and inflammation.
- Red Light Therapy can then improve the healing of acne lesions and repair skin damage caused by acne.
4. Treatment Regimens
- Sequential Use: You might use blue light therapy first to target acne and then follow with red light therapy to promote healing and rejuvenation.
- Combined Devices: Some devices are designed to deliver both red and blue light in a single treatment session, offering the convenience of a combined approach.
5. Consultation and Safety
Always consult with a dermatologist or skincare professional before starting any combined light therapy regimen. They can help tailor a treatment plan that suits your specific skin needs and ensure that the combination is safe and effective for you.
Blue light therapy is generally considered safe for most people, but when it comes to pregnancy, caution is advisable. Here’s what you need to know:
1. Limited Research on Pregnancy
There is limited research specifically examining the safety of blue light therapy during pregnancy. Because of this, its safety profile for pregnant women is not well-established.
2. Consult with Your Healthcare Provider
It’s essential to consult with your obstetrician or healthcare provider before undergoing any form of light therapy during pregnancy. They can provide personalized advice based on your health, medical history, and any specific concerns you might have.
3. Consider General Safety Precautions
While blue light therapy is non-invasive and uses light to treat skin conditions like acne, it’s still important to follow general safety precautions during pregnancy:
- Avoid Excessive Use: Use the therapy as recommended and avoid excessive exposure.
- Monitor Skin Sensitivity: Pregnancy can change your skin’s sensitivity. Monitor for any unusual reactions and adjust usage accordingly.
- Choose Reputable Devices: Ensure that the blue light therapy device is from a reputable source and follows safety standards.
4. Alternative Treatments
If you’re concerned about the safety of blue light therapy during pregnancy, discuss alternative treatments with your healthcare provider. There may be safer options available for managing skin conditions during this period.
Yes, you can generally exercise after blue light therapy. Blue light therapy primarily targets surface-level skin conditions, such as acne, and does not typically interfere with physical activity. However, there are a few considerations to keep in mind:
1. Allow Your Skin to Calm Down
Immediately after blue light therapy, your skin might be slightly red or sensitive. It’s a good idea to wait for any immediate post-treatment redness or sensitivity to subside before engaging in vigorous exercise.
2. Avoid Sweating Excessively
Heavy sweating during exercise can potentially irritate sensitive skin or exacerbate any post-treatment redness. If your skin is particularly sensitive after therapy, consider opting for a lighter workout or waiting until your skin has fully calmed.
3. Follow Post-Treatment Care
Ensure that you follow any specific post-treatment care instructions provided by your therapist or dermatologist. This might include applying gentle skincare products or avoiding certain activities.
4. Keep Clean
After exercising, make sure to cleanse your skin to remove sweat, bacteria, and any impurities that could clog pores or irritate sensitive skin.
5. Sun Protection
If you plan to exercise outdoors, make sure to apply sunscreen. Blue light therapy can make your skin more sensitive to UV rays, so protecting it from sun exposure is important.
Overall, exercising after blue light therapy is generally safe and should not impact the effectiveness of the treatment. Just be mindful of your skin’s condition and follow appropriate post-treatment care practices.
Red light therapy, also known as low-level laser therapy (LLLT), has shown promise in promoting gum health and potentially aiding in the regeneration of gum tissue. While it may not completely “regrow” gums in the way that they were before gum loss, it can help in the following ways:
1. Stimulating Cellular Activity
Red light therapy stimulates fibroblasts, the cells responsible for generating connective tissue, which is crucial for gum regeneration. It also promotes collagen production, which is essential for maintaining the structure and strength of gum tissue.
2. Reducing Inflammation
Gum inflammation is a common issue in periodontal disease. Red light therapy can reduce inflammation by increasing blood flow and decreasing the production of inflammatory cytokines, helping to create a healthier environment for gum tissue.
3. Enhancing Healing
Red light therapy accelerates the healing process of gum tissue by increasing cellular energy (ATP production) and promoting better oxygenation and nutrient delivery to the cells. This can support the healing of damaged gums and potentially slow down further gum recession.
4. Supporting Overall Oral Health
While red light therapy can contribute to better gum health, it’s most effective when used alongside good oral hygiene practices and professional dental care.
Clinical Evidence and Considerations
Some studies have shown positive outcomes in using red light therapy for gum health, but more extensive research is needed to fully understand its potential in gum regeneration. It’s important to consult with a dentist before starting red light therapy to ensure it’s appropriate for your specific condition.
Conclusion
Red light therapy may not entirely regrow lost gum tissue, but it can help improve gum health, reduce inflammation, and support tissue healing, making it a valuable adjunctive treatment in oral care.
Before using blue light therapy on your face, it’s important to prepare your skin properly to ensure the treatment is effective and safe. Here’s what you should consider:
1. Cleanse Your Face
Start with a gentle cleanser to remove any dirt, oil, and makeup from your face. This ensures that the light can penetrate your skin more effectively without any barriers.
2. Dry Your Skin
After cleansing, gently pat your face dry with a clean towel. Your skin should be completely dry before starting the therapy.
3. Apply a Serum (Optional)
Some blue light therapy users apply a serum designed for acne treatment or skin rejuvenation before the session. Make sure the serum is suitable for use with light therapy and doesn’t contain any light-sensitive ingredients that might cause irritation.
4. Avoid Light-Sensitive Products
Do not apply any products that contain retinoids, vitamin A, or other light-sensitive ingredients before blue light therapy, as these can make your skin more prone to irritation.
5. Sunscreen (After Treatment)
Blue light therapy doesn’t require sunscreen before treatment, but it’s a good idea to apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen after your session, especially if you’re going outside. Blue light can make your skin more sensitive to UV rays.
By following these steps, you can maximize the benefits of blue light therapy while minimizing any potential risks.