Thyroid issues are pervasive in modern society, affecting people of all genders and ages. Yet, they are often overlooked or misdiagnosed, with conventional treatments and prescriptions lagging far behind scientific understanding. The question red light therapy and thyroid we aim to answer in this article is whether red light therapy can play a role in the prevention and treatment of thyroid-related problems and low metabolism.
Introduction
Hypothyroidism, also known as low thyroid or underactive thyroid, is increasingly recognized not just as a condition affecting older adults but as a spectrum of dysfunction that nearly everyone can fall into to some degree. Modern society has made it clear that very few people possess truly ideal thyroid hormone levels. Hypothyroidism can overlap with a variety of metabolic issues like diabetes, heart disease, high cholesterol, IBS, and even depression or hair loss. In fact, having a “slow metabolism” is in essence the same as hypothyroidism, but it is diagnosed as clinical hypothyroidism only once thyroid hormone levels fall below a certain threshold.
At its core, hypothyroidism is the state of low energy production throughout the body due to insufficient thyroid hormone activity. This low energy output can result in a wide range of symptoms, which often coincide with other health conditions. Current treatments for hypothyroidism, largely based on hormone replacement therapy, may not address the underlying causes or optimize thyroid health effectively.
Recent studies have explored the potential of light therapy in alleviating thyroid dysfunction. By examining scientific literature, we find multiple studies suggesting that light therapy might not only aid in thyroid function but also play a role in managing low metabolism and related health issues.
Light Therapy Research on Thyroid Function
Light therapy, particularly red and infrared light, has been studied for its effects on various biological functions, including thyroid health. Research involving humans (Höfling et al., 2013), mice (Azevedo et al., 2005), and rabbits (Weber et al., 2014) demonstrates light therapy’s potential to influence thyroid hormone production and metabolism.
The primary mechanism behind these effects lies in light’s ability to stimulate mitochondrial activity. As the thyroid is crucial in energy production, applying red light therapy to the thyroid gland may improve its function by increasing cellular energy. Several studies suggest that light, especially in the 600-1000nm range (red and near-infrared), can break the vicious cycle of hypothyroidism by enhancing energy availability in thyroid tissues. This, in turn, could stimulate the production of thyroid hormones and improve overall metabolic function.
While red light (660nm) can penetrate the skin to some extent, infrared light 850nm) is more effective at reaching deeper tissues, making it ideal for thyroid treatment. The enhanced cellular energy could not only improve thyroid function but also trigger positive downstream effects, including better energy production throughout the body.

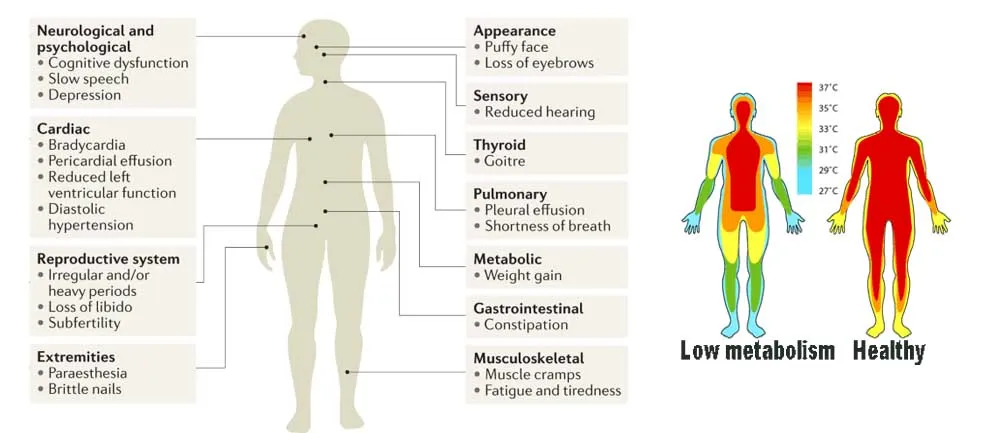
Symptoms of Low Metabolism and Hypothyroidism
When metabolism slows down due to an underactive thyroid, it can feel like body is running out of fuel. Here are some common signs that something might be off:
- Low energy levels: Do you feel tired no matter how much sleep you get? This constant fatigue can be a major clue.
- Cold hands and feet: If you’re always reaching for a sweater or your feet feel like ice blocks, it could be a sign of poor circulation caused by low thyroid activity.
- Slow heartbeat: A resting heart rate that’s too low (under 75 beats per minute) might mean your metabolism is dragging.
- Weight gain: Struggling to shed pounds despite eating well and exercising? A sluggish thyroid might be slowing down your body’s calorie burn.
- Dry, flaky skin: Your skin may feel rough and lose its natural glow due to poor hydration and reduced cell turnover.
- Hair thinning and brittle nails: Hair falling out or nails breaking easily can happen when your body doesn’t have enough energy to support healthy growth.
- Brain fog and memory issues: Struggling to focus or feeling forgetful? Low thyroid levels can leave your brain feeling fuzzy.
- Mood swings: Anxiety, depression, or irritability are common when your thyroid isn’t functioning properly.
- Digestive troubles: Slow digestion can lead to constipation, bloating, or discomfort.
- Low sex drive: Hormonal imbalances from a low thyroid can cause libido to take a hit.
These symptoms might seem random, but they all tie back to one thing: your body isn’t producing enough energy to function smoothly. If you notice a combination of these, it’s worth getting your thyroid checked out.
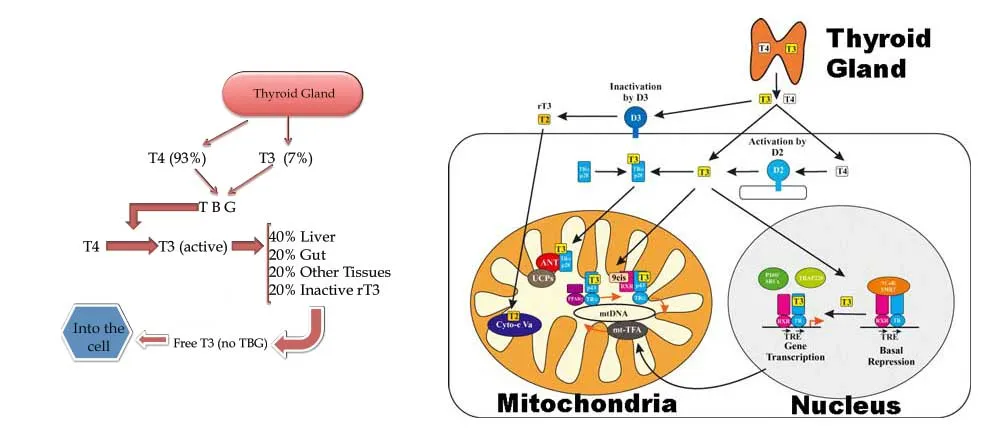
How Does the Thyroid System Work?
Thyroid is like body’s energy manager, controlling how every cell uses fuel. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
- The thyroid gland: This butterfly-shaped gland in your neck produces thyroid hormones, mainly T4 (thyroxine).
- Conversion to active hormone: T4 isn’t the hormone your cells use. It’s like an unripe fruit that needs to be converted into T3 (triiodothyronine), the active form your body needs. Most of this conversion happens in your liver and other tissues.
- T3 and your cells: Once converted, T3 enters your cells and “flips the switch” on your mitochondria—the tiny powerhouses inside each cell. This process boosts energy production and keeps everything running smoothly.
But when something goes wrong, this system can break down:
- If the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough T4, your whole energy supply takes a hit. This could happen due to autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto’s, iodine deficiency, or stress.
- If your liver or tissues don’t properly convert T4 to T3, the body can’t use the thyroid hormones effectively. Factors like a poor diet, lack of exercise, or too much stress can interfere with this step.
- Even if you have enough T3, your cells might not respond to it properly. This is often caused by inflammation, high levels of cortisol (a stress hormone), or too many unhealthy fats in your diet.
When thyroid system doesn’t work as it should, it’s like trying to drive a car with an empty gas tank. Energy stalls, and every system in body slows down.
Taking care of thyroid involves supporting each part of this system. That means eating nutrient-rich foods, managing stress, and sometimes exploring treatments like red light therapy to help thyroid gland work more efficiently.
Can Red Light Therapy Help Low Thyroid People?
Red and infrared light therapy is being studied for its potential to enhance thyroid function and metabolism. Red light therapy works by stimulating mitochondria, which are responsible for energy production in cells.
When applied to the thyroid gland, led red light therapy might improve local energy production, helping to stimulate the thyroid to produce more hormones. This could potentially break the cycle of low thyroid hormone levels, where low energy leads to reduced thyroid activity and vice versa. Studies have shown that light therapy can increase local ATP (adenosine triphosphate) production in the thyroid cells, thus enhancing their function.
Furthermore, red and infrared light may also exert systemic effects through the bloodstream. While red blood cells do not contain mitochondria, platelets, white blood cells, and other cells do, which means light exposure could potentially reduce inflammation, lower cortisol (a stress hormone that inhibits thyroid function), and improve overall metabolic function.
In addition, red light therapy may have a localized effect when applied to specific areas of the body, such as the neck or skin, promoting healing and reducing inflammation in the thyroid. This approach could complement the natural functions of thyroid hormone, promoting a healthy metabolism and reducing the symptoms of hypothyroidism.

Red Light Therapy for Thyroid Function
So, let’s talk about red light therapy and how it might help with thyroid function. It sounds like something out of a science fiction movie, but it’s actually a real and pretty cool treatment that’s gaining attention for its potential health benefits, including for thyroid health.
How Does Red Light Therapy Work?
Red light therapy (RLT) uses specific wavelengths of light, usually in the range of 600 to 950nm, to penetrate your skin and reach deeper tissues. Think of it like your cells are getting a “boost” of energy directly from the light. This energy helps your cells, especially in areas like the thyroid gland, work more efficiently.
When you shine red or infrared light on your neck (where the thyroid is located), it can help in several ways:
- Increased Energy for Cells: The light boosts the energy production inside your cells, especially in the mitochondria (the powerhouse of the cell). Healthy thyroid cells need energy to produce thyroid hormones. So, more energy could mean your thyroid starts functioning better, possibly increasing the amount of thyroid hormone it produces.
- Improved Blood Flow: Red light can improve blood circulation, which helps deliver more oxygen and nutrients to your thyroid gland. This can help it perform better and may even promote healing if the thyroid is damaged or inflamed.
- Reducing Inflammation: When you have thyroid issues, inflammation often plays a role. Red light therapy can help reduce inflammation around the thyroid gland. By decreasing inflammation, your thyroid might be able to work more efficiently and produce the hormones your body needs.
- Regulating Hormones: Light therapy may also affect other hormone systems. For example, studies suggest it can lower stress hormones like cortisol, which can interfere with thyroid function. Less stress means your thyroid might perform better overall.
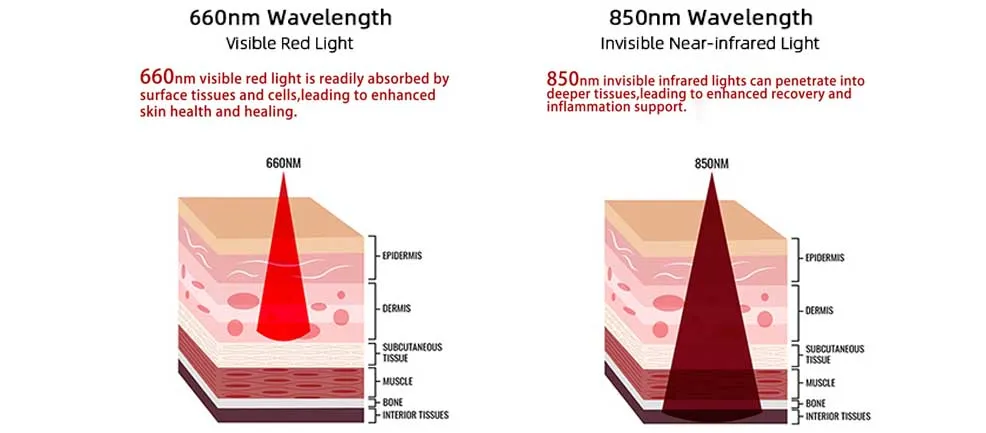
Why Red and Infrared Light to Thyroid?
The thyroid is located in the neck, just under the skin, so it’s a relatively accessible spot for light therapy. While there are lots of different types of light, red and infrared light are most commonly used for thyroid issues because they penetrate deep enough into the skin to reach the thyroid but are also safe and effective.
- Red Light (660nm): Red light can penetrate the skin and reach the thyroid tissue. It’s useful for stimulating surface-level processes, like improving blood flow and reducing inflammation.
- Infrared Light (8950nm): Infrared light has a longer wavelength, so it can penetrate even deeper into the tissues, helping improve cellular energy production and metabolism at a deeper level. This is why infrared light might be especially helpful for the thyroid, as it reaches the gland more directly.
What the Research Says
There have been a number of studies showing that light therapy can have a positive effect on thyroid health. For example:
- One study (Höfling DB, 2010) found that light therapy using red and infrared light improved thyroid function in patients with autoimmune thyroiditis (a common thyroid disorder).
- Another study (Azevedo LH et al., 2005) in mice found that red light had a beneficial effect on thyroid function by stimulating hormone production.
- In human trials, red light therapy has shown potential in improving thyroid hormone levels and reducing symptoms of hypothyroidism (low thyroid function). By boosting the energy and health of the thyroid cells, red light therapy might help restore balance to thyroid hormones, especially in cases where there’s low production.
How to Use Red Light Therapy for Thyroid Health
If you’re considering using red light therapy for thyroid issues, here are some things to keep in mind:
- Target the Neck Area: You’ll want to focus the light on your neck, where the thyroid is located. The treatment is usually done for 10-20 minutes per session. You can use a red light device or an infrared light panel. There are also portable handheld devices available that can be used on the thyroid area.
- Consistency is Key: Like most therapies, red light therapy requires consistency to see noticeable results. You might want to try using the therapy a few times a week and see how it affects you over time.
- Look for Specific Wavelengths: For maximum benefit, it’s best to use lights in the 600-950nm range. Infrared lights in the 700-910nm range are particularly effective for thyroid treatment, but red light in the 630-650nm range can still offer benefits, especially for surface-level effects.
- Use Safe, Quality Devices: Make sure you’re using a device that’s safe and specifically designed for light therapy. Cheap alternatives or DIY methods may not offer the right wavelength or intensity to be effective.
Conclusion
Red and infrared light therapy has shown potential in improving thyroid function and addressing low metabolism. Light therapy works by stimulating cellular energy production, reducing inflammation, and improving thyroid hormone production. It offers a promising complement to traditional therapies for hypothyroidism, especially when combined with lifestyle and dietary improvements.
As the thyroid system is complex, addressing thyroid health requires a multi-faceted approach. Diet, stress management, and red light therapy can all play crucial roles in supporting thyroid function and metabolic health.
Recommended Light Therapy Devices
For individuals looking to explore red light therapy for thyroid health, infrared LEDs in the 700-910nm range, mostly 850nm are the most studied and recommended. Devices with a power density of 100mW/cm² or higher, and appropriate treatment durations, are most effective for thyroid therapy.
References
Höfling, DB, et al. (2010) – Effect of low-level laser therapy on the thyroid gland in patients with autoimmune thyroiditis:
Azevedo, LH, et al. (2005) – Effects of low-level laser therapy on thyroid function in mice:
Orellana, et al. (2018) – Photobiomodulation (PBM) in hypothyroidism: A literature review of its potential benefits:
Karu, T. (2010) – Mitochondrial mechanisms of photobiomodulation in context of different cell types and tissues:
A Gupta. (2014) – Effects of red and infrared light on wound healing and cell metabolism:
MR Hamblin (2017) – Mechanisms of photobiomodulation in the treatment of inflammation and autoimmune diseases:
Fitzgerald, T., & Dennis, C. (2020) – A review of the clinical applications of light therapy for thyroid conditions: